Have you ever wondered if all gas caps are interchangeable? The simple answer is no – gas caps are designed with specific compatibility factors for different vehicles. Using the wrong gas cap can lead to serious issues with your vehicle’s fuel system, trigger check engine lights, and even impact emissions and fuel efficiency.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about gas cap compatibility, from identifying the right cap for your vehicle to understanding the consequences of using an incompatible one. Whether you’re replacing a lost cap or troubleshooting a check engine light, this information will help you make the right choice for your vehicle.
Why Gas Cap Compatibility Matters
Your vehicle’s gas cap might seem like a simple component, but it plays several crucial roles in your vehicle’s operation. Using a compatible gas cap is essential for:
- Maintaining proper fuel system pressure
- Preventing fuel evaporation and improving fuel economy
- Controlling harmful emissions from escaping into the atmosphere
- Keeping contaminants out of your fuel tank
- Preventing check engine light warnings related to EVAP system issues
Modern vehicles have sophisticated evaporative emission control (EVAP) systems that rely on a properly sealed fuel system. An incompatible or poorly fitting gas cap can trigger the check engine light and potentially lead to failed emissions tests. According to EPA estimates, replacing faulty gas caps could save millions of gallons of fuel annually that would otherwise evaporate into the atmosphere.

Different Types of Gas Caps by Vehicle Type
Gas caps vary significantly across different vehicle categories. Understanding these differences is the first step in identifying the right replacement cap for your vehicle.

Passenger Cars
Most modern passenger cars use threaded gas caps that create a seal with a rubber gasket. These typically require 2-3 turns to tighten properly and often make an audible “clicking” sound when fully secured. Many newer models feature tethered caps to prevent loss.

Trucks & Commercial Vehicles
Trucks and commercial vehicles often use larger, more robust gas caps designed to withstand frequent use and harsher conditions. These may have different thread patterns and sealing mechanisms compared to passenger vehicles.

Motorcycles
Motorcycle gas caps are typically smaller in diameter and often feature locking mechanisms for security. Many use a bayonet-style mounting system rather than threads, requiring a quarter-turn to secure.

Specialty Vehicles
ATVs, snowmobiles, and recreational vehicles often use specialized gas caps with unique venting systems designed for their specific operating conditions. These are rarely interchangeable with automotive caps.
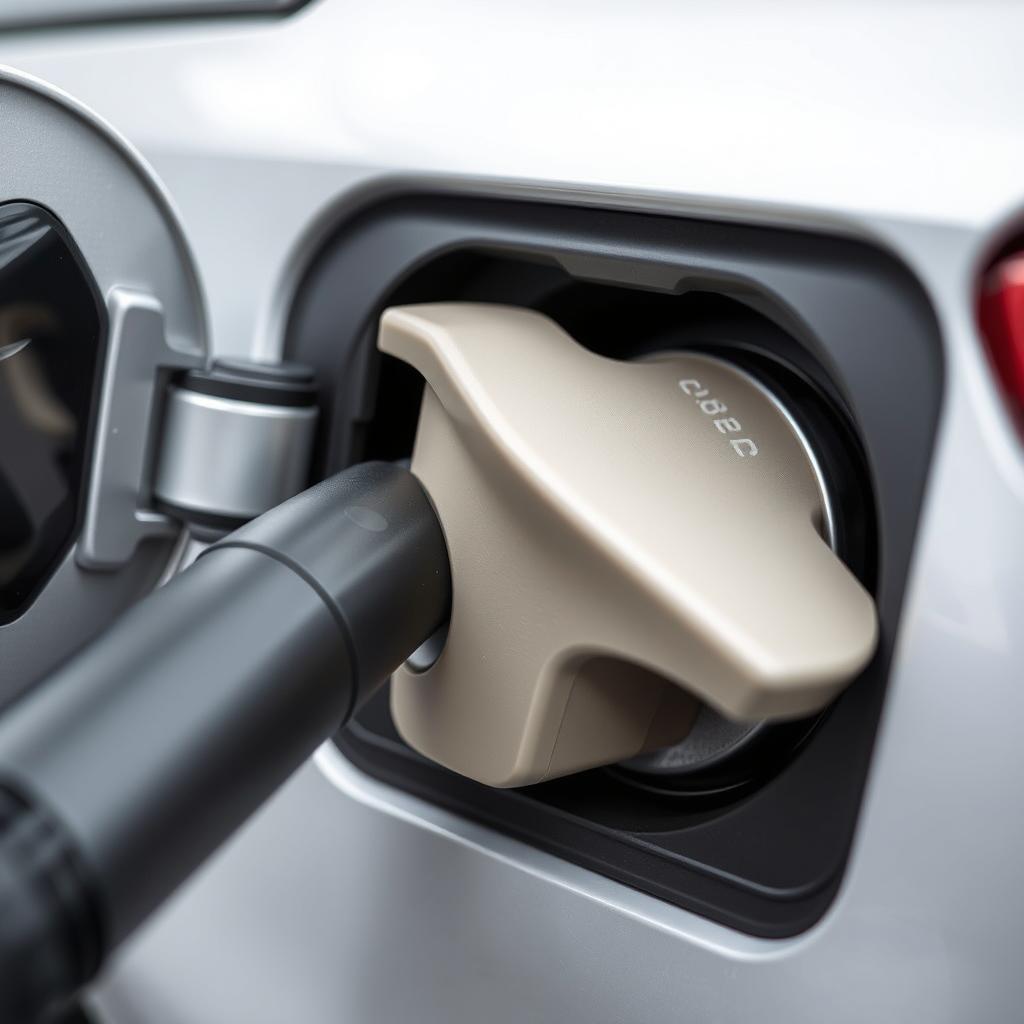

Capless Systems
Many newer vehicles use capless fuel systems (also called Easy Fuel) that eliminate the traditional gas cap entirely. These systems use internal flaps that open when the fuel nozzle is inserted and seal automatically when removed.

Vintage/Classic Vehicles
Older vehicles often have unique gas cap designs that may be difficult to find direct replacements for. These can range from simple non-vented caps to decorative chrome-finished caps that are part of the vehicle’s aesthetic.
Key Compatibility Factors for Gas Caps
Several critical factors determine whether a gas cap will be compatible with your vehicle. Understanding these elements will help you identify the correct replacement cap.

Thread Size and Pattern
The most important compatibility factor is the thread size and pattern. Gas caps use specific thread dimensions (diameter and pitch) that must match your vehicle’s fuel filler neck exactly. Even slight variations can prevent proper sealing or secure attachment.
Thread patterns are typically manufacturer-specific, meaning Toyota caps generally won’t fit Ford vehicles, and European vehicle caps often differ from American or Asian models. Some examples of common thread sizes include:
| Vehicle Make | Common Thread Size | Compatible With |
| Toyota/Lexus | 77mm x 4.5 pitch | Most Toyota, Lexus models 2000-2010 |
| Honda/Acura | 80mm x 5.0 pitch | Most Honda, Acura models 1998-2012 |
| Ford/Lincoln | 87mm x 4.0 pitch | Most Ford, Lincoln models 2003-2015 |
| GM Vehicles | 82mm x 3.5 pitch | Most Chevrolet, GMC, Buick 2005-2018 |
Material Composition
Gas caps are typically made from high-density plastic with rubber gaskets, but material quality and composition vary. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) caps often use higher-grade materials designed to withstand temperature extremes and exposure to fuel vapors without degrading.
The gasket material is particularly important, as it creates the seal that prevents fuel vapors from escaping. Lower-quality gaskets may deteriorate faster, especially in regions with extreme temperatures or high humidity.

Pressure Release Mechanisms
Modern gas caps incorporate pressure release valves that maintain proper pressure in the fuel tank. These mechanisms are calibrated to specific pressures for each vehicle model and must function correctly to prevent fuel system damage.
The pressure release system typically consists of:
- Vacuum relief valve: Allows air to enter the tank as fuel is consumed
- Pressure relief valve: Releases excess pressure if the tank becomes over-pressurized
- Torsion spring: Controls the opening and closing of these valves
Using a gas cap with incorrect pressure specifications can lead to fuel system problems, including hard starting, rough idling, and potential damage to the evaporative emissions system.
OEM vs. Aftermarket Gas Caps: Making the Right Choice
When replacing your gas cap, you’ll typically choose between OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) caps and aftermarket alternatives. Each option has distinct advantages and potential drawbacks.
OEM Gas Caps: Pros
- Guaranteed exact fit for your specific vehicle
- Identical to your original cap in function and appearance
- Engineered to meet manufacturer specifications for pressure relief
- Often more durable with higher-quality materials
- Usually includes warranty coverage from the vehicle manufacturer
OEM Gas Caps: Cons
- Typically more expensive (often 2-3 times the cost of aftermarket)
- May only be available through dealerships
- Limited options for customization or upgrades
- Can be difficult to source for older or discontinued models
Aftermarket Gas Caps: Pros
- Significantly lower cost in most cases
- Widely available through auto parts stores and online retailers
- Some offer enhanced features like better grips or improved sealing
- Available for older vehicles where OEM parts are discontinued
- Options for locking caps and other security features
Aftermarket Gas Caps: Cons
- Quality can vary significantly between manufacturers
- May not perfectly match OEM pressure relief specifications
- Can trigger check engine lights if not precisely compatible
- Often made with lower-grade materials that may deteriorate faster
- Limited warranty coverage in many cases

For most vehicles, an OEM gas cap provides the most reliable performance and longevity. However, quality aftermarket caps from reputable manufacturers can offer satisfactory performance at a lower price point, especially for older vehicles or temporary replacements.
How to Identify the Correct Gas Cap for Your Vehicle
Finding the right gas cap for your specific vehicle doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are several reliable methods to ensure you purchase a compatible replacement:
Using Your Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
Your VIN contains coded information about your vehicle’s specifications, including compatible parts. This 17-character code can be found:
- On the driver’s side dashboard (visible through the windshield)
- On the driver’s side door jamb sticker
- On your vehicle registration and insurance documents
With your VIN, you can:
- Contact your dealership parts department for the exact OEM cap part number
- Use online parts lookup tools that cross-reference your VIN with compatible parts
- Provide the information to auto parts stores for accurate compatibility matching

Consulting Your Owner’s Manual
Your vehicle’s owner’s manual often contains specific information about replacement parts, including the gas cap. Look in the maintenance or specifications section for:
- OEM part numbers for common replacement items
- Specifications for the fuel system components
- Instructions for proper gas cap installation and tightening
Using Dealership Parts Systems
Vehicle dealerships have access to comprehensive parts databases that can identify the exact gas cap for your specific model, year, and even production date. This is particularly valuable for vehicles with mid-year design changes or special editions that might have unique specifications.
Online Parts Compatibility Tools
Many auto parts retailers and online marketplaces offer vehicle-specific lookup tools where you can enter your make, model, year, and sometimes engine type to find compatible parts. These systems typically access extensive databases of cross-referenced part numbers to ensure compatibility.
Checking Your Current Gas Cap
If your current gas cap is still available, check for identifying information such as:
- Part numbers molded into the plastic (often on the underside or edge)
- Manufacturer logos or branding
- Thread size indicators (sometimes marked in millimeters)
This information can be used to find an exact replacement or to cross-reference with compatible alternatives.
Consequences of Using Incompatible Gas Caps
Using a gas cap that isn’t compatible with your vehicle can lead to a range of problems, from minor inconveniences to potentially serious issues. Understanding these consequences can help emphasize the importance of finding the right replacement.
Evaporative Emissions Issues
Modern vehicles have sophisticated Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) systems designed to prevent fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. An incompatible gas cap can compromise this system by:
- Creating an improper seal that allows fuel vapors to escape
- Failing to maintain the correct pressure in the fuel tank
- Interfering with the EVAP system’s ability to perform self-tests
These issues can trigger the check engine light and store diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the EVAP system, such as P0440, P0442, or P0455. These codes specifically indicate evaporative system leaks that are often traced back to gas cap problems.

Fuel System Problems
The fuel system in your vehicle relies on proper pressure regulation, which can be disrupted by an incompatible gas cap. Potential issues include:
- Hard starting due to improper tank pressure
- Reduced fuel economy from evaporating fuel
- Fuel pump strain from working against incorrect pressure
- Contamination of the fuel system from inadequate sealing
Failed Emissions Tests
In areas with vehicle emissions testing, an incompatible gas cap can lead to failed tests. Many testing facilities specifically check for proper gas cap sealing as part of their procedure, and some will even test the cap’s ability to maintain pressure.
Safety Hazards
While less common, there are potential safety concerns with incompatible gas caps:
- Fuel leakage in the event of a vehicle rollover
- Increased fire risk from fuel vapor leaks
- Caps that don’t secure properly could come loose while driving
Important Safety Note: Never attempt to modify a gas cap to fit your vehicle or use makeshift solutions like tape or sealants. These temporary fixes can create dangerous situations and potentially damage your fuel system.
Testing Gas Cap Compatibility and Proper Installation
Before purchasing a replacement gas cap, or to verify if your current cap is functioning correctly, you can perform several tests to check compatibility and proper sealing.
Visual Inspection
- Examine the gas cap for any visible damage, cracks, or deterioration of the rubber gasket
- Check that the threading is clean and undamaged
- Verify that any pressure relief valves or vents are clear and functioning
- Look for signs of warping or deformation that might prevent proper sealing
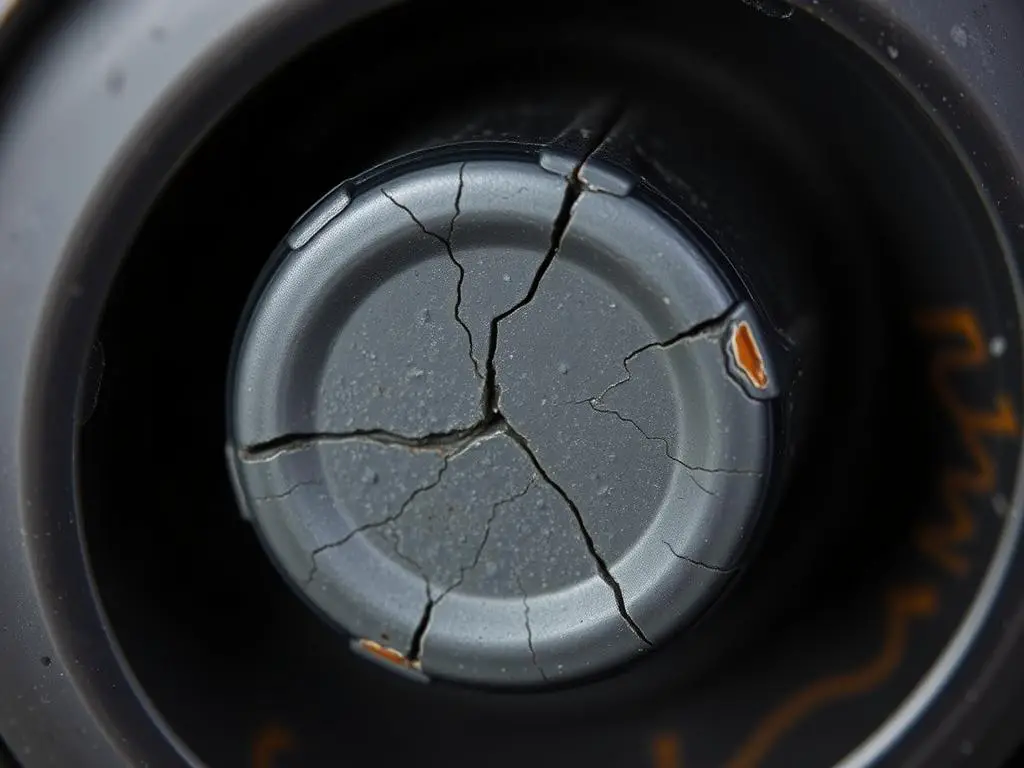

Proper Installation Test
Follow these steps to ensure your gas cap is properly installed:
- Position the cap squarely on the filler neck
- Turn clockwise until you hear clicking sounds (typically 3-4 clicks)
- The cap should feel secure and not loose after tightening
- If tethered, the tether should not be stretched tight when the cap is secured
If the cap doesn’t tighten properly, spins freely without clicking, or feels loose after tightening, it may be incompatible or damaged.

Check Engine Light Test
If your check engine light is on due to a suspected gas cap issue:
- Tighten the gas cap properly (until it clicks)
- Drive the vehicle for 50-100 miles to allow the system to run its self-tests
- If the light remains on, have the codes read with an OBD-II scanner
- Codes P0440, P0442, or P0455 often indicate gas cap issues
Professional EVAP System Test
For the most definitive test, a professional mechanic can perform a smoke test of the EVAP system, which can precisely identify leaks around the gas cap or filler neck. This test involves introducing harmless smoke into the fuel system and observing where it escapes.
Special Considerations for Locking Gas Caps
Locking gas caps provide an additional layer of security for your vehicle’s fuel system. However, they come with special compatibility considerations beyond those of standard caps.
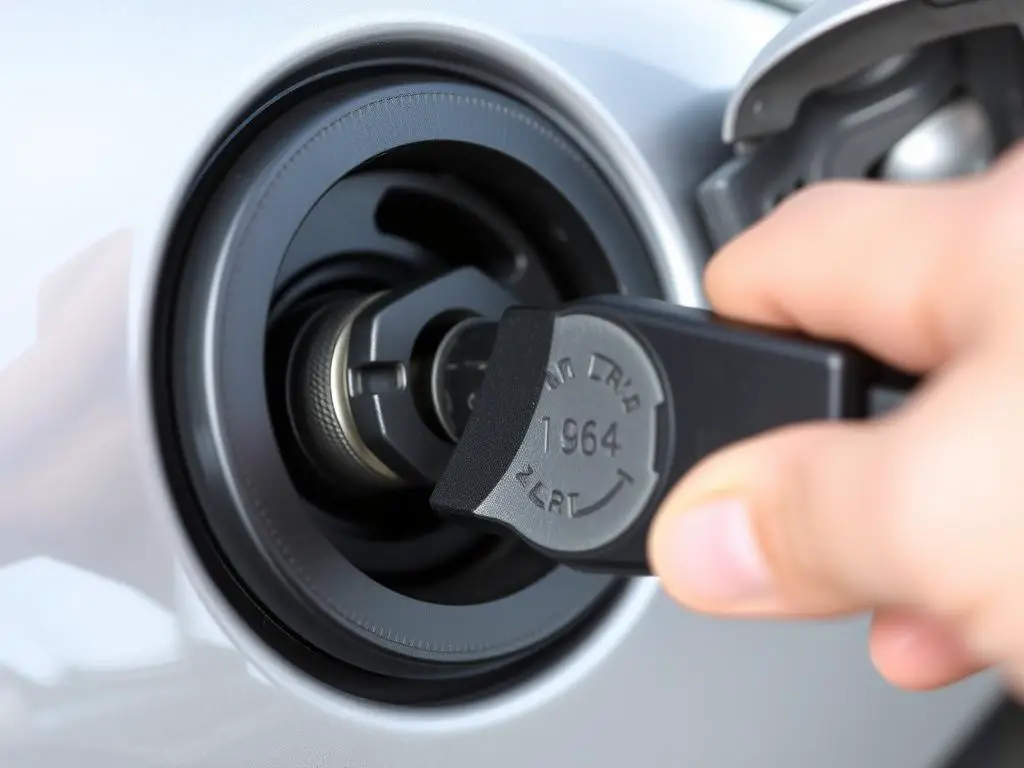

Types of Locking Mechanisms
Locking gas caps typically use one of these security systems:
- Key Lock: Requires a specific key to unlock the cap for removal
- Combination Lock: Uses a user-set numerical code for unlocking
- Integrated Vehicle Security: Some newer vehicles integrate fuel door locking with the central locking system
Compatibility Challenges
When selecting a locking gas cap, consider these additional compatibility factors:
- The locking mechanism adds bulk that may interfere with the fuel door closing
- Some vehicle models have recessed filler necks that limit the size of cap that will fit
- The additional weight of locking mechanisms can strain the threading on plastic filler necks
- Locking caps may not include the same pressure relief features as OEM caps
Anti-Siphoning Features
Many locking gas caps also include anti-siphoning features to prevent fuel theft. These typically consist of:
- Metal screens or baffles that block siphon tube insertion
- One-way valve systems that allow fuel in but not out
- Narrow-throat designs that restrict access to the fuel tank
When selecting a cap with anti-siphoning features, ensure it won’t interfere with refueling or cause splashback when filling the tank.
“While locking gas caps can provide theft protection, they must still maintain proper sealing and pressure relief functions to avoid triggering check engine lights or causing fuel system issues.”
Gas Cap Maintenance and Replacement Indicators
Even the highest quality gas caps eventually wear out and require replacement. Knowing when and how to maintain your gas cap can extend its life and help you recognize when replacement is necessary.
Signs Your Gas Cap Needs Replacement
Watch for these indicators that your gas cap may need to be replaced:
- Check engine light with EVAP system codes (P0440, P0442, P0455)
- Visible damage to the cap or gasket (cracks, tears, deformation)
- Cap doesn’t “click” when tightening or feels loose after tightening
- Fuel odor around the vehicle, especially near the filler area
- Failed emissions test with gas cap identified as the issue
- Tether broken or cap missing entirely
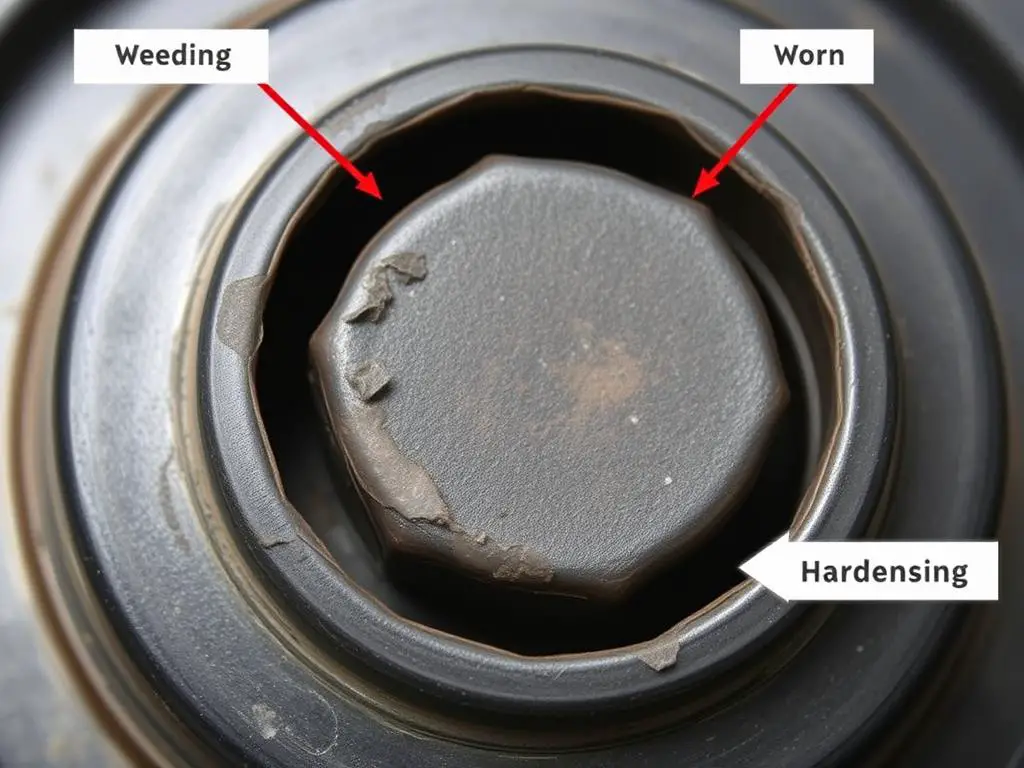
Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your gas cap:
- Periodically clean the cap and threads with a clean, dry cloth
- Inspect the rubber gasket for signs of wear or deterioration
- Avoid overtightening, which can damage the gasket and threading
- Keep the filler neck area clean to prevent debris from affecting the seal
- In cold climates, prevent ice buildup around the cap area
Replacement Frequency Guidelines
While there’s no fixed schedule for gas cap replacement, these guidelines can help:
| Vehicle Age/Usage | Recommended Inspection | Typical Replacement Interval |
| New vehicles (0-5 years) | Annual visual inspection | Only if damaged or check engine light appears |
| Mid-life vehicles (5-10 years) | Inspect every 6 months | Every 5-7 years or when signs of wear appear |
| Older vehicles (10+ years) | Inspect quarterly | Every 3-5 years or at first sign of deterioration |
| High-mileage vehicles (100k+ miles) | Inspect with every oil change | Every 2-3 years as preventative maintenance |
Pro Tip: Many mechanics recommend replacing your gas cap as preventative maintenance when your vehicle reaches 100,000 miles, even if it shows no obvious signs of wear. This can help prevent check engine lights and ensure optimal fuel system performance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gas Cap Compatibility
Are gas caps universal across all vehicle makes and models?
No, gas caps are not universal. They vary in thread size, pattern, pressure relief specifications, and physical dimensions depending on the vehicle make, model, and year. Using a cap from a different vehicle can cause check engine lights, failed emissions tests, and potential fuel system issues.
Can I use a gas cap from a different year of the same vehicle model?
Sometimes, but not always. Manufacturers occasionally change gas cap specifications between model years, even for the same vehicle. It’s best to verify compatibility using your VIN or consult with a dealership parts department to ensure the cap will work properly with your specific model year.
Will any locking gas cap fit my vehicle?
No, locking gas caps must match the same thread pattern and size as your vehicle’s standard cap. Additionally, some locking caps may be too bulky for vehicles with small fuel door compartments or recessed filler necks. Always check compatibility specifically for locking caps, as they have additional dimensional considerations.
How do I know if my check engine light is related to my gas cap?
The most common indicator is an EVAP system code when the check engine light is scanned. Codes P0440, P0442, and P0455 frequently relate to gas cap issues. You can test this by ensuring your cap is properly tightened, clearing the code, and driving for 50-100 miles. If the light doesn’t return, the gas cap was likely the culprit.
Are aftermarket gas caps as reliable as OEM caps?
Quality varies significantly among aftermarket caps. High-quality aftermarket caps from reputable manufacturers can perform adequately, but they may not match the exact pressure relief specifications of OEM caps. For critical applications or vehicles with sensitive emissions systems, OEM caps typically provide the most reliable performance and longevity.
Can I drive without a gas cap temporarily?
It’s not recommended. Driving without a gas cap will almost certainly trigger your check engine light, reduce fuel economy due to evaporation, allow contaminants into your fuel tank, and potentially create a fire hazard. If you lose your gas cap, purchase a universal temporary cap until you can get the correct replacement.
How do capless fuel systems work, and can they be converted to use caps?
Capless fuel systems use internal spring-loaded flaps that open when the fuel nozzle is inserted and close automatically when removed. While adapters exist to convert capless systems to accept traditional gas caps (useful for using portable fuel containers), these should be used temporarily and removed for normal refueling to maintain the integrity of the capless system.
Conclusion: The Importance of Proper Gas Cap Compatibility
While a gas cap might seem like a simple component, its role in your vehicle’s fuel and emissions systems is significant. Using a compatible, properly functioning gas cap is essential for maintaining fuel efficiency, preventing check engine lights, passing emissions tests, and protecting your fuel system.
When replacing your gas cap, take the time to verify compatibility using your VIN, vehicle specifications, or professional guidance. The small investment in the correct cap can prevent larger issues down the road and help keep your vehicle running at its best.
Remember that gas caps do wear out over time, so periodic inspection and timely replacement when signs of deterioration appear will help maintain your vehicle’s performance and reduce environmental impact through proper emissions control.


